From Tennis Elbow to Bursitis: Navigating Nine Chronic Elbow Injuries

Your elbows work overtime. Whether you’re playing sports, working at a desk, or lifting objects, the bones, muscles, and tendons in your elbows are constantly in use. According to orthopedic elbow specialists, this wide range of motion also makes elbows susceptible to numerous injuries. Some acute injuries can result from single incidents, like falling or getting hit during contact sports. Chronic elbow pain can stem from wear-and-tear injuries or conditions like osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis.
Here are the Nine Most Common Chronic Elbow Injuries
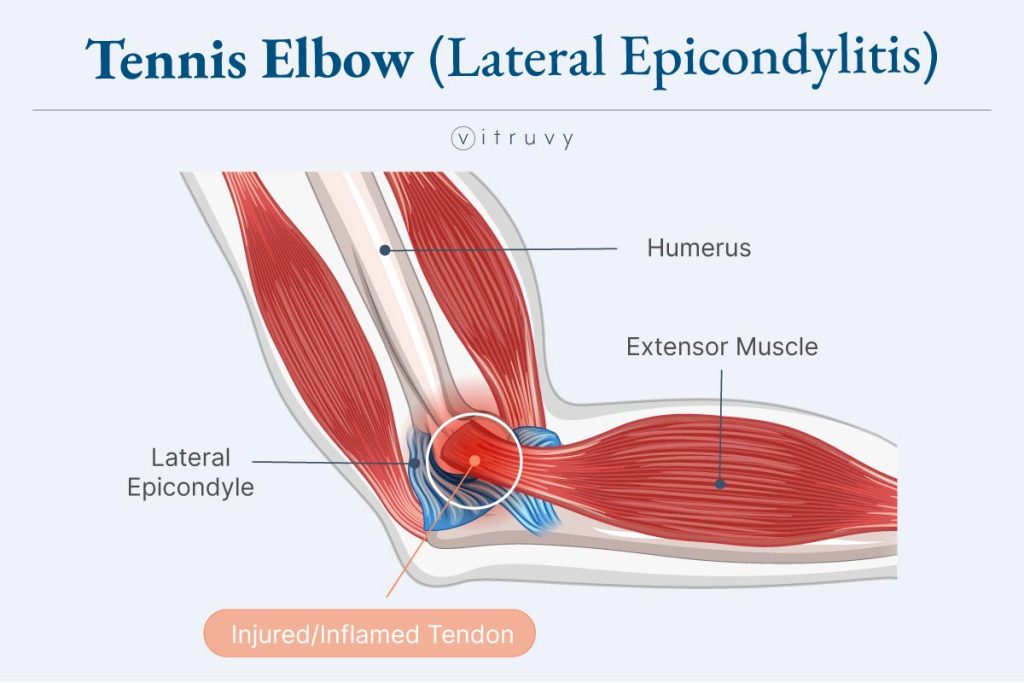
Tennis Elbow (Lateral Epicondylitis)
Inflammation of the tendons on the outside of the elbow, causing pain and tenderness.
Tennis Elbow Anatomy
Overuse injury causing pain on the outside of the elbow, often due to repetitive wrist and arm motions, as illustrated below:
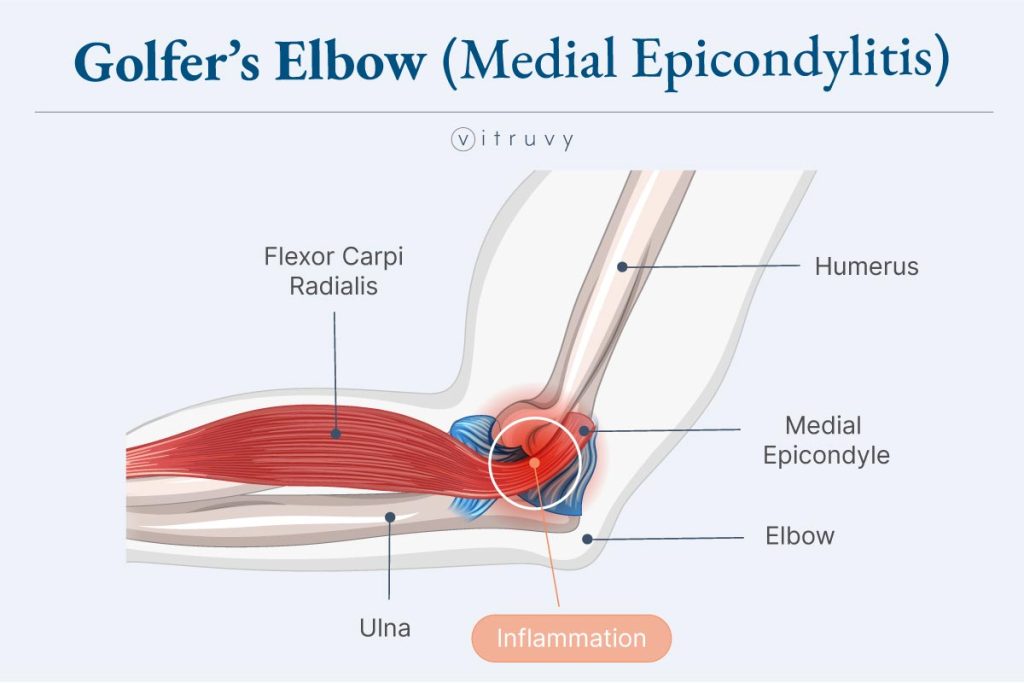
Golfer's Elbow (Medial Epicondylitis)
A type of tendonitis that results in pain and inflammation of the tendons connecting the forearm to the elbow. This condition can impact the ability to flex and rotate the wrist and forearm. Initially, symptoms often present as minor pain or tenderness on the inner elbow. As the condition progresses, the pain can radiate up and down the arm.
Anatomy of Golfer's Elbow
Similar to tennis elbow, but the pain is located on the inside of the elbow as illustrated below.
Bursitis
The elbow bursa (olecranon bursa) is a fluid-filled sac that cushions your bones, muscles, and tendons. Infection or repetitive movements can irritate or damage the bursa, leading to swelling and pain. People with physically demanding jobs, musicians, and athletes are particularly susceptible to bursitis. Even common activities such as gardening, painting, and shoveling can cause bursitis. Most non-infectious cases of elbow bursitis are treated at home over three to six weeks with rest, over-the-counter non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), and joint immobilization.
Cubital Tunnel Syndrome
Compression of the ulnar nerve at the elbow, causing numbness, tingling, and pain in the forearm and hand.
Osteoarthritis (OA)
Commonly the result of “wear-and-tear” on the joint or prior traumatic injury, osteoarthritis causes pain and stiffness in the elbow when the cartilage wears down and bone rubs against bone.
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)
The most common type of arthritis in the elbow. Most people are familiar with the idea that rheumatoid nodules affect the fingers, but did you know they can also develop on the tips of your elbows? RA causes elbow instability, pain, and difficulty bending or straightening the elbow.
Ulnar Collateral Ligament (UCL) Injury
Damage to the ligament on the inside of the elbow, common in throwing athletes.
Osteochondritis Dissecans
A condition where a fragment of bone and cartilage separates from the end of the bone, causing pain and joint instability.
Triceps Tendinitis
Inflammation of the triceps tendon at the back of the elbow, causing pain and swelling.
Is Chronic Hand or Finger Pain Stopping You From Doing What You Love?
In less than 5 minutes, our assessment tells you and our orthopedic partner specialists where you are on your healthcare journey. Based on your answers you can instantly schedule an appointment with a specialist who understands your pain and your lifestyle.
